[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”3.22″][et_pb_row _builder_version=”3.25″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”3.25″ custom_padding=”|||” custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.27.4″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”]
Type 2 diabetes has become a major public health problem and characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period of time. If left untreated it can cause serious long-term complications like retinopathy, neuropathy, chronic kidney diseases, heart attacks, stroke, foot ulcers leading to amputation and cognitive impairment. About 450 million people worldwide have diabetes, the majority living in low-and middle-income countries. India has 77 million with diabetes. Also, 1.6 million deaths are directly attributed to diabetes each year. The problem is further magnified by the fact that the age of onset of diabetes in India is a decade earlier than the rest of the world and the burden of undetected diabetes is also very high.
Psychological stress also increases the risk and severity of diabetes. Lifestyle strategy which facilitates in reducing physical inactivity, impaired sleep, depression, stress, dysfunctional habits, which are commonly seen in type 2 diabetes is critical for its management apart from the standard medical management. At this juncture, there is a need for a complementary treatment like Yoga which warrants cost-effective, preventive and management strategies for type 2 diabetes.
Yoga – the ancient mind and body discipline
Yoga, which originated in India more than 5,000 years ago, aims at balancing and harmonizing the body, mind, and emotions. Research over the past three decades on yoga has consolidated the evidence in supporting it as a mind –a body-oriented practice that promotes “relaxation response” which reduces stress promotes positive coping skills. Yoga being a multi-component practice with Asanas (postures), Pranayama (breath regulation). Dhyana (Focusing and Contemplation) and other lifestyle discipline is a holistic approach and intervention strategy to address many psycho physiological issues.
Yoga and diabetes
Yoga has been widely advocated in India for the management of diabetes, hypertension and related chronic conditions. Yoga as an intervention varies widely. Many conceptualize yoga as a physical intervention incorporating body postures (asanas), breathing techniques (pranayama), meditation, modification of attitudes and behavior along mental discipline. in mobilization.
Many controlled trials on yoga for diabetes indicate that yoga may promote improvement in certain clinical parameters such as glycemic index, lipid Levels, weight, etc. Some studies have reported psychological well-being and better quality of life in the same target groups. Yoga, which includes both dynamic and static postures along with regulated breathing i.e., pranayama makes a person-oriented and alters the mental status of an individual.
There has been positive evidence stating that yoga practices are beneficial in improving specific clinical parameters which are important for type 2 diabetes management. Research on yoga and type 2 diabetes has shown a lot of beneficial effects both in physical, psychological, social and overall well-being in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Yoga helps in parasympathetic activation, overall metabolic and psychological profiles, increase insulin sensitivity and improve glucose tolerance and lipid metabolism. Yoga practices such as cleansing processes, asanas, pranayama, mudras, bandha, meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation are known to reduce blood glucose levels and to help in the management of comorbid disease conditions associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, resulting in significant positive clinical outcomes.
Yoga and mindful eating:
Yoga is also known to regulate eating patterns, and its potential utility in the management of eating disorders has been advocated. Yoga and pranayama are found to be beneficial in improving dietary practices and medication adherence. Yoga participation has been correlated with both fruit and vegetable intake, as well as improved eating habits and mindful eating practices. Mindful eating in diabetes has shown to facilitate improvements in dietary intake, modest weight loss, and glycaemic control.
Role of Asanas and Pranayama:
Asanas emphasize the relationship of body, mind and breath. Physical movements involve stretching/twisting. All yoga postures should be performed with stability and comfort. Pranayama is a controlled or regulated yogic breathing practice that helps in controlling the autonomic nervous system; it regularizes the rate and pattern of breathing and regulates the heart rate and its variability.
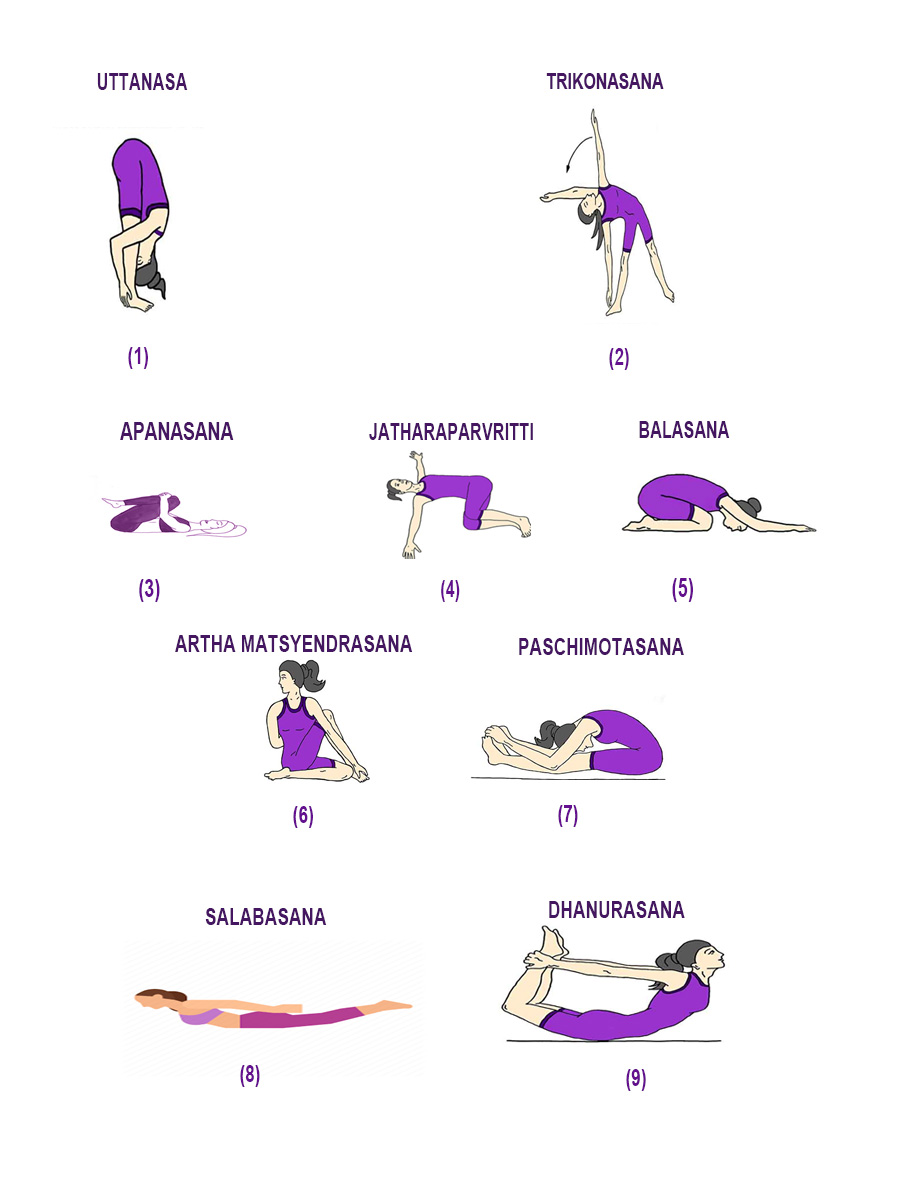
Few asanas for diabetes and general well-being : ( Illustrated below- Figure:1)
Standing postures: Uttanasa, Trikonasana twist
Lying postures: Apanasana, Jatharaparvritti, Balasana
Sitting postures.: Artha matsyendrasana, paschimotasana.
Prone Postures : Dhanurasana and Salabasana
Pranayama: Anuloma Viloma (Alternate nostril breathing), Bhramari ( Bee Breath, Bhastrika ( Bellow Breath) and Sitali ( cooling)
All these to be practiced under the guidance of a yoga teacher.
Yoga to be learned from a qualified teacher:
Yoga should be learned from a qualified yoga professional. A relatively safe yoga style suitable for an individual’s requirements should be practiced. Patients taking medication to control diabetes should carefully monitor their bodies’ reactions to any new fitness activity. Yoga is recommended to be done on empty stomach but those taking treatments for diabetes are encouraged to take light snacks in order to prevent hypoglycemia.
Table 1:
[wptb id=9638]
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]